LoRaWAN is a global standard for Low Power Wide Area (LPWA) IoT Networks
What is LoRa Technology and LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is a Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) protocol, built on top of Semtech’s LoRa wireless RF and promoted by the LoRa Alliance, that supports long range, low-cost, mobile, energy-efficient, deep indoor penetration and secure end-to-end bi-directional communication for Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine to Machine (M2M) applications. Running on unlicensed ISM frequencies worldwide, this connectivity is specifically dedicated to IoT use cases and allows cost efficient deployments and operations for both public or private networks.
What are the benefits of LoRaWAN?

Long Range
LoRaWAN provides robust long-range communication (up to 40 km in rural areas and up to 3 km in urban environment, and depending on gateways performances) between sensors on the field and radio network stations.
Low Power
LoRaWAN was designed to specifically reduce the power consumption and extend the battery lifetime of connected sensors, up to 10+ years
Fully Bidirectional
LoRaWAN enables fully bidirectional communications that can support many use cases that require both uplinks and downlinks, either with limited random receive windows (Class A), with limited scheduled receive slots (Class B), or with maximal and almost continuous receive slots (Class C).

Native Geolocation
LoRaWAN offers secure network-based geolocation to locate any LoRa-enabled fixe or mobile end-device. LoRa uses Time Differential on Arrival and other hybrid techniques to determine location without using extra processing power on the end-device side. This native capability, unlike GPS, does not increase energy consumption, nor needs additional costly hardware component.

Deep Indoor Penetration
LoRa radio modulation allows deep indoor penetration, making it possible to reach energy meters, controls modules in elevators shafts, or parking sensors located in basements and undergrounds.

Free Unlicensed Band
LoRaWAN networks operates on license-free and cost-free ISM (Industrial, Scientific, Medical) bands – EU 868 MHz, AS 923 MHz, US 915 MHz – allowing any service provider or company to deploy and operate networks without acquiring a license from the regulator.
Open Standard
LoRaWAN standard leverages an open protocol approach, led by the LoRa Alliance which federates the specification, development and deployment of the standard, elaborates certification guides, and ensures interoperability between all radio infrastructure providers, core network vendors and end-devices designers and manufacturers.

Cost Efficiency
LoRaWAN open standard, high performance infrastructure, and value-added connectivity services enables public or private operators to deploy and operate networks quickly, with streamlined capital expenditure (Capex) and operational expenses (Opex), and achieve a fast time to market to benefit from the IoT expansion in various segments.

Security
LoRaWAN offers two future-proof layers of end-to-end security:
one for the network that ensures mutual authentication between a LoRaWAN end-device and the LoRaWAN network as part of the network join procedure. This grants that network traffic has not been altered, only comes for a legitimate end-device authorized to join an authentic network, is not comprehensible to eavesdroppers, and has not been captured and replayed by rogue actors.
one for the application that ensures the network operator does not have access to the end user’s application data. LoRaWAN is one of the few IoT network implementing end-to-end encryption for application payloads exchanged between the end-devices and applications servers. In traditional cellular networks, the traffic is encrypted over the air interface but transmitted as plain text in the operator’s core network, requesting the user to select and deploy an additional security layer (VPN or dedicated security layer encryption application).
LoRa Alliance “Full end-to-end encryption for IoT Applications Providers” LoRaWAN Security white-Paper
LoRa Alliance LoRaWAN Security FAQ
Scalability
LoRaWAN offers high scalability and capacity networks to support thousands of connected end-devices and millions of messages transmitted. This high performance is achieved by utilizing Adaptive Data Rate (ADR) and by using a multi-channel multi modem transceiver in the gateway so that simultaneous messages on multiple channels can be received.

LoRaWAN Network Infrastructure
LoRaWAN IoT Network Snapshot
A LoRaWAN IoT Network is deployed following! a star of stars network architecture whereby IoT sensors and end-devices are not associated with a specific gateway but transmit data to multiple gateways within it radio range.
IoT Sensors and End-Devices
IoT device manufacturers and OEMs can efficiently resort to LoRa Alliance global and regional specifications and parameters, as well as its certification programs to design IoT sensors and end-devices that will connect to IoT LoRaWAN networks. They can also achieve a faster time to market by leveraging existing Reference Design guidelines proposed by some vendors, based on their expertise of IoT LoRaWAN networks, to efficiently embed LoRaWAN IoT connectivity in their design, get best practices to optimize sensor and device connection and data transmission over the IoT network.
IoT Radio Network
LoRaWAN gateways, designed for outdoor coverage and indoor connectivity, can independently support tens of thousands of IoT sensor and end-devices and enable public and private IoT networks deployments. The LoRa gateways support bi-directional communication and can simultaneously process messages from many LoRa-based IoT sensor and end-devices. The LoRaWAN gateways act as packet forwarders and send packets to a LoRa Network Server (aka LNS) through a backhaul connection that may use Ethernet, Wi-Fi, 3G, 4G or LTE-M / NB-IoT. LoRa gateways are far less expensive compared to cellular base stations and use free unlicensed frequencies in all geographies, making the increase of the network capacity really flexible, scalable and affordable by simply adding additional IoT gateways, in an easy way. LoRaWAN gateways can support between 8 to 64 channels, which allows millions of messages per day processed by such an IoT network. The quality of the radio network (coverage, robustness, performance, up-time, availability, and reliability) directly depends on the quality of the gateways and their industrial- grade design and carrier-grade optimization.
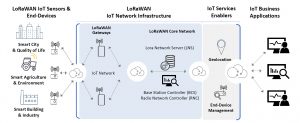
IoT Core Network
The LNS (LoRaWAN Network Server) can be hosted in the cloud or deployed in the operator premises. It processes packets received from multiple IoT gateways, then directing them to an application server through secured links. Deploying and operating a performant LoRaWAN IoT network requests powerful tools to monitor, optimize, manage or troubleshoot the radio configuration, the IoT gateways operations and their configuration, and grant the requested IoT network QoS. Inspired by cellular network experience, some LoRaWAN vendors are offering a full suite of management solutions – Operations Support System (OSS) -, to efficiently orchestrate the entire IoT network in real-time, and ensure its perfect design and availability for mission critical data collection. On top of LoRaWAN Network Server (LNS), Base Stations Controller (BSC) is a key set of features to remotely operate the LoRa gateways deployed on the field (settings, alerts firmware and application update, security, integrity), whereas Radio Network Controller (RNC) helps to constantly monitor and optimize radio performances and coverage of the entire IoT network (frequencies, spectrum, spreading factors, power, load…).
IoT Application Servers
The LoRaWAN Network Server (LNS) send packets to the appropriate application server which powers the customer business application and process the data to make them relevant and actionable for decision-making. Radio Access Network capabilities can also be integrated directly in IoT applications servers and dashboards through APIs (best vendors are delivering API-first design for their network software management tools), for quickly setting up, integrating and managing a LoRaWAN IoT network. Business owners can also enrich application server capabilities with value added services like geolocation or end-device management, to make the most of radio and core network capabilities, and create new services generating offer differentiation and additional revenue streams.



